
|
|
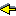
Flag |
Values |
Description |
ISO |
bounded |
true / false |
are integers
bounded ? |
Y |
max_integer |
an integer |
greatest integer |
Y |
min_integer |
an integer |
smallest integer |
Y |
integer_rounding_function |
toward_zero
down |
rnd(X) = integer part of X
rnd(X) = lfloorXrfloor (section 7.6.1) |
Y |
max_arity |
an integer |
maximum arity for compound terms (255) |
Y |
max_atom |
an integer |
maximum number of atoms |
N |
max_unget |
an integer |
maximum number of successive ungets |
N |
prolog_name |
an atom |
name of the Prolog system |
N |
prolog_version |
an atom |
version number of the Prolog system |
N |
prolog_date |
an atom |
date of the Prolog system |
N |
prolog_copyright |
an atom |
copyright message of the Prolog
system |
N |
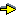
Flag |
Values |
Description |
ISO |
char_conversion |
on / off |
is
character conversion activated ? |
Y |
debug |
on / off |
is the debugger
activated ? |
Y |
singleton_warning |
on / off |
warn
about named singleton variables ? |
N |
strict_iso |
on / off |
strict ISO
behavior ? |
N |
double_quotes |
atom chars codes atom_no_escape chars_no_escape codes_no_escape |
a double quoted constant is returned as:
an atom a list of characters a list of character codes as atom but ignore escape sequences as chars but ignore escape sequences as code but ignore escape sequences |
Y N |
back_quotes |
atom chars codes atom_no_escape chars_no_escape codes_no_escape |
a back quoted constant is returned as:
an atom a list of characters a list of character codes as atom but ignore escape sequences as chars but ignore escape sequences as code but ignore escape sequences |
N |
unknown |
error warning fail |
a predicate calls an unknown procedure:
an existence_error is raised a message is displayed then fails quietly fails |
Y |
syntax_error |
error warning fail |
a predicate causes a syntax error:
a syntax_error is raised a message is displayed then fails quietly fails |
N |
os_error |
error warning fail |
a predicate causes an O.S. error:
a system_error is raised a message is displayed then fails quietly fails |
N |
| Flag is a variable | instantiation_error | ||
| Value is a variable | instantiation_error | ||
| Flag is neither a variable nor an atom | type_error(atom, Flag) | ||
| Flag is an atom but not a valid flag | domain_error(prolog_flag, Flag) | ||
| Value is inappropriate for Flag | domain_error(flag_value, Flag+Value) | ||
| Value is appropriate for Flag but flag Flag is not modifiable | permission_error(modify, flag, Flag) | ||
|
| Flag is neither a variable nor an atom | type_error(atom, Flag) | ||
| Flag is an atom but not a valid flag | domain_error(prolog_flag, Flag) | ||
|
| Functor is a variable | instantiation_error | ||
| Arity is a variable | instantiation_error | ||
| Functor is neither a variable nor an atom | type_error(atom, Functor) | ||
| Arity is neither a variable nor an integer | type_error(integer, Arity) | ||
|
| Functor is neither a variable nor an atom | type_error(atom, Functor) | ||
| Arity is neither a variable nor an integer | type_error(integer, Arity) | ||
|
| FileName is a variable | instantiation_error | ||
| FileName is neither a variable nor an atom | type_error(atom, FileName) | ||
| an operating system error occurs and the value of the os_error Prolog flag is error (section 7.22.1) | system_error(atom explaining the error) | ||


